ERP
- Home
- ERP
ENERGY RELATED PRODUCTS
Since September 2015, new EU regulations have been implemented energy related products, including space heating and hot water supply devices.
These new regulations aim at energy efficiency, cleaner pollutants, and easier and more accurate information for the consumers and end users of the related products (in our case boilers).
In this new era has begun and all water boilers will have to meet the demands which are derived from the regulations: 813/2013 (Eco Design), and 811/2013 (Energy Labelling).
If you want to know more you can check out the following links for the full text:
Regulation 813/2013,
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32011R0813&qid=1537769364804&from=EN
Regulation 811/2013,
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32013R0811&qid=1537769044736&from=EN

A. ECO DESIGN
Regulation 813/2013
Using Eco-Design for a product means designing the product, (in our case a boiler), with two main criteria:
A’1. The energy that the product (boiler) consumes during its operation, but also,
A’2. The energy and materials required for its construction.
Regulation 813/2013 deals with the Manufacturers, Importers and Distributors of boilers who are also responsible under the Certification Act of the boilers.
It is obvious that ECO DESIGN leads us to products more “friendly” to the environment and more economical in their operation. In case of boilers, the high requirements for the annual thermal performance of a boiler set by the regulation drives us to the use of condensing technology.
A Few Words About Condensing Technology.
Up to now, conventional boilers released exhaust gases of temperatures from 160 to 200 degrees Celsius, which resulted in large amounts of wasted thermal energy in the environment. Condensing technology exploits all this latent energy of the exhaust gases and returns most of this back to the heating water circuit. This is accomplished either through an appropriate combustion chamber, or by using external stainless steel heat exchangers (OSCAR technology) with which the boilers operate.
The BOILER results in the exhaust gas temperature being reduced to such an extent that the condensation effect of the exhaust fumes is generated.
For gaseous fuels the condensation temperature (dew temperature) is 57° C, while for petroleum is 47° C.
The condensation product is “water” which contains acidic pollutants which are collected by a condensate neutralizer and then led to the drainage network.

Β. ENERGY LABELLING
Regulation 811/2013
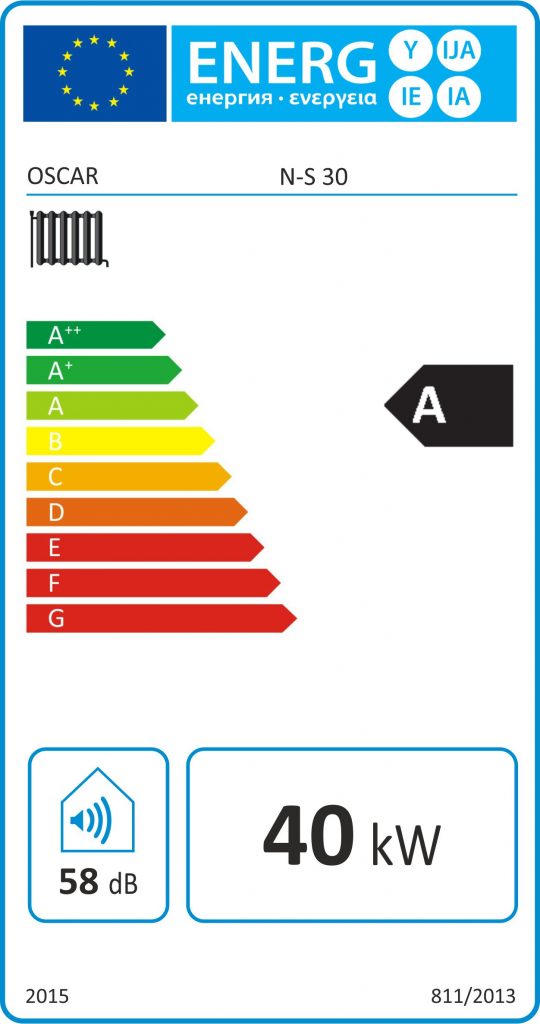
The energy labelling is exclusively for CONSUMERS and is intended to provide information on the ENERGY EFFICIENCY OF THE PRODUCT (BOILER).
It is applicable to boilers of less than 70 kW, nominal power.
The goal of energy labeling is to promote energy-efficient products. For this purpose, a user-friendly Energy Label was created containing all this information.
Thus, the consumer with a simple reading can be informed:
● The energy class of the boiler and compare it directly with it
competition even if it cannot correlate the degree of performance with the
specific numbers, e.g. easily recognizes that Class A is clearly better
Class B, and so on,
● The manufacturer,
● The boiler’s power output,
● Noise level of the boiler,
● If the boiler is only for heating (radiator body icon) or for hot water use (tap icon),
etc.
OSCAR Boilers have been one of the first manufacturers to fully comply with all of the above regulations, offering a full range of condensing boilers, as well as heat exchangers that can convert your existing boilers to condensing ones.
Search for an OSCAR product in your area and rest assured that you use a state-of-the -art, environmental friendly, energy efficient product.